Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common developmental problem that affects millions of children, teens, and adults. It can be difficult to diagnose correctly but is typically characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness.
ADHD: Background
According to current estimates:
- 1 in 5 high school boys has ADHD.
- 11 percent of school-aged children over-all has a current diagnosis of ADHD.
- 60 percent of children with ADHD will continue to have symptoms into adulthood.
- 4 percent of the adult US population is affected by ADHD (roughly 8 million adults).
- More men are diagnosed with ADHD than women.
- There is a shortage of psychiatrists who specialize in the diagnosis treatment of ADHD.
Rise In ADHD Diagnosis: Cause for Concern?
In the past decade, the number of children and teens being diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has risen by 66 percent. Some experts believe this increase is a welcome sign, indicating that the medical community is effectively recognizing and treating the symptoms of ADHD in children and teens who suffer from debilitating symptoms that negatively affect their performance in school.
Other doctors, researchers, and patient advocates, however, are not so easily convinced. They see the steep increase in diagnoses as a sign that ADHD is being seriously over diagnosed and over treated with powerfully addictive psychostimulant medications that carry a high risk of addiction and abuse.
While it is true that the diagnosis and treatment of ADHD are not without controversy when children, teens, and adults who suffer from ADHD do receive proper diagnosis and treatment, they are able to control their symptoms and function more effectively at school, work and home.
More Diagnoses of ADHD Causing Concern – New York Times
Parents whose children receive an ADHD diagnosis are often confused, and unsure whether the risks of using powerful psychostimulant medications to treat ADHD symptoms outweigh their benefits. Recent studies indicate that psychostimulants were used in 96 percent of ADHD treatments in 2000 but fell to 87 percent in 2010. Although the exact reason for this decrease is not clear, other medications were not used in substitution. This could mean that children, teens and adults who need treatment are not receiving the help they need, but studies have not reached any definitive conclusion on the matter.
Adults and ADHD
Adults who suffer from ADHD typically exhibit difficulty concentrating, organizing tasks, following directions, remembering information and completing work within appropriate time limits. If their symptoms are not treated, they can suffer confusing and difficult consequences that affect their social, emotional, and academic lives. Their career prospects may suffer. Undiagnosed ADHD can also be at the root of long-standing difficulties relating to co-workers, friends, and family. Studies show that fewer adults with ADHD are treated for their symptoms because many mistakenly believe that ADHD is a “children’s” disorder.
The consequences of ignoring the symptoms of adult ADHD are serious because it is a disorder that affects so many aspects of adult functioning. Adults with untreated ADHD are more likely to engage in a variety of risky behaviors and are more likely to have substance abuse problems. Adults with symptoms of ADHD should consult a qualified physician who can assess and diagnose their condition so that they can receive proper help and treatment.
Adults who have been diagnosed with ADHD are statistically more likely to:
- Have suspended licenses.
- Have been cited for driving violations (such as speeding).
- Rate themselves as having poorer driving habits.
- Use illegal substances more frequently.
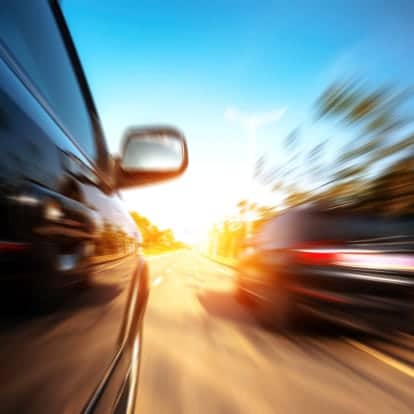
Study Shows ADHD Tied to More Traffic Accidents
According to a recent study of Swedish drivers, men with ADHD who were being treated with ADHD medication were 58 percent less likely to be involved in a traffic accident when they were taking ADHD medication. Researchers also found that men who were taking ADHD medication were 29 percent less likely to be involved in a serious traffic accident while taking their medication.
No substantial difference in risk for traffic accidents was found for women who were being treated with ADHD medication, but researchers noted that fewer women were involved in the study overall, so the numbers reflected by the study may not have been accurate.
For the study, researchers collected data on Swedish drivers between 2006 and 2009. During that time frame, there were approximately 214 serious accidents for every 10,000 men with ADHD each year. In that same time frame, there were about 77 serious accidents per 10,000 men without ADHD.
Researchers suspect that because ADHD typically involves an increase in inattention and impulsivity, distracted driving and dangerous driving behaviors may increase when drivers are not receiving appropriate treatment for their ADHD symptoms.
Distracted Driving and ADHD
Distracted driving puts all motorists at increased risk for serious traffic related crashes in injuries, and should be avoided at all costs. According to the DISTRACTION.GOV site:
- At any given daylight moment across America, approximately 660,000 drivers are using cell phones or manipulating electronic devices while driving.
- Engaging in visual-manual subtasks (such as reaching for a phone, dialing, and texting) associated with the use of hand-held phones and other portable devices increased the risk of getting into a crash by three times.
No driver should engage in any behavior that takes their focus off the road and their driving and endangers other drivers. AAA notes that distracted driving accounts for 25 to 50% of all traffic accidents.
For teens and adults with ADHD, it is especially important to avoid distracted driving. Any of the following behaviors can distract a driver, causes an accident.
- Texting
- Using a cell phone or smartphone
- Eating and drinking
- Talking to passengers
- Grooming
- Reading, including maps
- Using a navigation system
- Watching a video
- Adjusting a radio, CD player, or MP3 player
Not all drivers with ADHD are distracted or poor drivers. But if a driver has ADHD or untreated ADHD, it may cause an increase in distracted driving or impulsivity. A diagnosis of ADHD should be taken very seriously. If you suspect you or a loved one has ADHD, consult a qualified physician for assessment and treatment.
If you have been injured in an automobile accident and you suspect distracted or impaired driving may be a factor, please call the experienced and caring personal injury attorneys at Hardy, Wolf and Downing. Our Maine personal injury attorneys understand how to approach distracted driving cases, answer your questions about insurance companies and get you the compensation you deserve for your injuries. Being injured in a car accident is traumatic and painful, and not something you need to deal with on your own. Let the personal injury attorneys of Hardy, Wolf and Downing fight for your rights, and get you the just and fair compensation you deserve for your pain and suffering.